#how to reverse a string in python
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Reversing a string is an important concept across multiple domains. Below are some of the important reasons to know the significance of reversing a string.
0 notes
Text
Lists in python
Lists in Python are a type of sequence data type. They are mutable, meaning that they can be changed after they are created. Lists can store elements of any type, including strings, integers, floats, and even other lists.
Lists are represented by square brackets ([]) and contain elements separated by commas. For example, the following code creates a list of strings:
Python
my_list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
Lists can be accessed using indices, which start at 0. For example, the following code prints the first element of the list my_list:
Python
print(my_list[0])
Output:
apple
Lists can also be sliced, which allows you to extract a subset of the list. For example, the following code prints a slice of the list my_list that contains the first two elements:
Python
print(my_list[0:2])
Output:
['apple', 'banana']
Lists can be modified by adding, removing, or changing elements. For example, the following code adds an element to the end of the list my_list:
Python
my_list.append("orange")
The following code removes the first element of the list my_list:
Python
my_list.pop(0)
The following code changes the second element of the list my_list:
Python
my_list[1] = "pear"
Lists can be used to perform a variety of tasks, such as storing data, iterating over data, and performing data analysis.
Here are some examples of how to use lists in Python:
Python
# Create a list of numbers numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # Print the list print(numbers) # Add an element to the list numbers.append(6) # Remove an element from the list numbers.pop(0) # Sort the list numbers.sort() # Reverse the list numbers.reverse() # Iterate over the list for number in numbers: print(numbers)
Output:
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] [2, 3, 4, 5, 6] [3, 4, 5, 6] [6, 5, 4, 3] 3 4 5 6
Lists are a powerful tool for working with collections of data in Python. They can be used to perform a variety of tasks, such as storing data, iterating over data, and performing data analysis.
#progblr#studyblr#learning to code#codetober#programmer#kumar's python study notes#python#coding#programming#codeblr
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
Coding Brushup for Python Beginners: 10 Fun and Easy Challenges
Python is known for its simplicity, readability, and power, making it one of the most beginner-friendly programming languages in the world. Whether you're just starting your Python programming journey or returning after a break, a structured coding brushup can help strengthen your foundational knowledge and boost your confidence.

This blog post highlights 10 fun and easy Python coding challenges designed to refresh core concepts and enhance your problem-solving skills. These challenges are not just practical exercises—they’re essential stepping stones for anyone looking to advance in Python development.
Let’s explore why coding brushup for Python is so valuable for beginners and walk through the types of challenges you should tackle.
Why Do a Coding Brushup for Python?
A coding brushup serves as a focused review that helps solidify what you’ve already learned. If you’ve taken a break from coding, just finished a Python course, or want to prepare for interviews or projects, revisiting the basics through hands-on challenges can work wonders.
Here are a few benefits of a coding brushup for Python beginners:
Reinforces Syntax and Logic: Python is known for clean syntax. Brushing up helps avoid common mistakes.
Builds Muscle Memory: The more you type and solve problems, the more intuitive Python programming becomes.
Boosts Confidence: Even easy challenges can be motivating and reinforce that you're making progress.
Prepares for Interviews: Basic Python coding questions are commonly asked in technical interviews.
Encourages a Growth Mindset: Regular practice keeps your brain in “learning mode,” which is key for long-term success.
1. Brush Up on Variables and Data Types
Every Python programming journey starts with understanding variables and data types. A coding brushup that focuses on assigning and manipulating data types like int, float, string, and bool helps form the building blocks of any program.
Challenge focus: Refresh your understanding of how Python handles data, casting between types, and using type functions.
2. Conditionals and Logic Statements
Decision-making is a crucial concept in programming. In this challenge, brush up on using if, elif, and else statements to control the flow of your Python code.
Why it matters: Practicing logic-based challenges sharpens your problem-solving mindset and enhances your decision-making ability within code.
3. Loops and Repetition
Loops like for and while are central to automation in Python programming. Brushing up on loops helps in writing efficient, repetitive code with minimal effort.
Challenge tip: Focus on simple loops that print patterns, calculate sums, or iterate over lists.
4. List and Array Operations
Lists are one of the most versatile and widely used data structures in Python coding. A good coding brushup for Python includes creating, modifying, and looping through lists.
Learning benefit: Understand slicing, appending, removing elements, and iterating through list items with ease.
5. String Manipulation
Strings appear in nearly every Python application. Brushing up on how to work with strings—concatenation, slicing, and built-in methods—is a must for every Python beginner.
Practical tip: Practice challenges involving reversing strings, finding substrings, or checking for palindromes.
6. Functions and Reusability
Functions allow for modular, reusable code. As part of your coding brushup, revisit how to define and call functions, pass arguments, and return results.
Why it's important: Functions make your Python code clean, organized, and easier to maintain.
7. Dictionaries and Key-Value Pairs
Dictionaries in Python allow you to store data in key-value pairs. For beginners, brushing up on dictionary creation, access, and iteration is both fun and rewarding.
Coding brushup focus: Try tasks that involve counting words, storing user data, or mapping values.
8. User Input and Output
Interacting with users through input() and displaying results with print() is fundamental. This type of challenge is perfect for reinforcing basic I/O operations in Python programming.
Real-world relevance: Many beginner projects involve taking input and responding with meaningful output.
9. Basic Error Handling
Even simple Python programs can crash due to unexpected input or logic errors. A coding brushup for Python should include understanding try, except, and how to handle common exceptions.
Why it matters: Handling errors makes your code more robust and user-friendly.
10. Working with Loops and Nested Logic
Combining loops and conditionals creates more powerful programs. Brush up with challenges that involve nested loops, such as generating patterns or multi-layered logic checks.
Challenge insight: These problems help deepen your logical thinking and prepare you for intermediate-level tasks.
Tips to Get the Most Out of Your Python Coding Brushup
To fully benefit from these beginner-friendly challenges, consider the following tips:
Practice Regularly: Set aside dedicated time for your coding brushup sessions.
Work Without Looking: Try solving problems without looking at previous code or online examples.
Reflect and Revise: After solving a challenge, take time to understand what you did well and what you can improve.
Document Your Learning: Keep a simple notebook or digital log to track your Python programming progress.
Stay Curious: Ask “what if” questions—what if I used a different loop? What if I changed the data type?
Why These Challenges Are Perfect for Beginners
Unlike complex algorithm problems that can intimidate newcomers, the above challenges focus on core programming principles using Python’s clean and intuitive syntax. They're short, focused, and effective, making them ideal for a quick coding brushup.
They also help reinforce the types of skills most commonly tested in entry-level roles, coding bootcamps, and university coursework. If you're serious about mastering Python programming, regular brushups like these will keep your skills fresh and growing.
Final Thoughts
Whether you're preparing for your first Python project or brushing up before a coding interview, these 10 fun and easy challenges offer the perfect opportunity to refresh and refine your knowledge. A well-structured coding brushup for Python beginners keeps you on track and helps you build the confidence needed to tackle more advanced problems in the future.
Remember, mastery comes from consistent practice, not from memorization. So embrace these challenges, enjoy the learning process, and take pride in every small improvement you make in your Python coding journey.
0 notes
Text
🧠 Python Trick: Reverse a String in ONE Line!
Ever written a loop to reverse a string? Something like:
reversed_text = ""
for char in text:
reversed_text = char + reversed_text
It works... but there's a smarter way.
👉 Use slicing instead:
print(text[::-1])
Why does it work?
[::–1] means slice the whole string, backwards.
🎥 Watch how it works in under 1 minute →
youtube
👇 Drop a 🔥 if you didn’t know this trick!
📲 Save & Share with your coding squad
#PythonTips #CodeLife #ProgrammingReels #DevTricks #LearnPython #PythonReels
0 notes
Text
Encryption and Information Security

As our lives and businesses become increasingly digital, protecting sensitive information has never been more critical. Encryption and information security play a vital role in safeguarding data from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and data breaches. This post explores the fundamentals of encryption, security strategies, and how developers can implement protection in their applications.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is the process of converting readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) using an algorithm and a key. Only those with the correct key can decrypt and access the original data.
Types of Encryption
Symmetric Encryption: Uses the same key for encryption and decryption (e.g., AES, DES).
Asymmetric Encryption: Uses a public key to encrypt and a private key to decrypt (e.g., RSA, ECC).
Hashing: Converts data into a fixed-length string; used for data verification, not reversible (e.g., SHA-256).
Common Use Cases
Securing communications (HTTPS, email)
Protecting stored data (databases, files)
User authentication and password protection
Digital signatures and certificates
Secure financial transactions and blockchain
Basic Encryption Example in Python (AES)
from Crypto.Cipher import AES import base64 key = b'ThisIsASecretKey' # 16 bytes cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_EAX) nonce = cipher.nonce ciphertext, tag = cipher.encrypt_and_digest(b'Confidential Data') print("Encrypted:", base64.b64encode(ciphertext))
What is Information Security?
Information security (InfoSec) is the practice of preventing unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, or destruction of data. It includes policies, practices, and technologies to protect digital and physical assets.
Pillars of Information Security (CIA Triad)
Confidentiality: Ensures data is accessible only to authorized users.
Integrity: Ensures data remains accurate and unaltered.
Availability: Ensures data and services are accessible when needed.
Best Practices for Developers
Use HTTPS and SSL/TLS for data transmission
Encrypt sensitive data in databases and files
Use secure password hashing (e.g., bcrypt, Argon2)
Regularly update and patch software dependencies
Implement access control and user authentication
Log and monitor activity for anomalies
Popular Tools and Libraries
OpenSSL: Toolkit for SSL/TLS encryption
PyCryptodome: Cryptographic library for Python
GnuPG: Open-source encryption tool for emails and files
OWASP ZAP: Security testing tool for web applications
Compliance and Legal Considerations
Follow regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS
Use encryption standards approved by NIST
Be transparent with users about data collection and protection
Conclusion
Encryption and information security are essential components of any modern software system. Whether you're a developer or a tech-savvy user, understanding how to protect data can help prevent devastating cyber incidents. Start applying encryption techniques and InfoSec principles to make your applications and digital life more secure.
0 notes
Text
Data Structures & Algorithms Udemy Free Download - GetFreeCourses

Most of my students know me for my practical, project-based courses and tutorials. I wanted to create something to give you more fundamental skills for problem solving. That’s where the idea for this challenges course came from. I want to take my down-to-earth explanations to help you get a better understanding of the code that you write and help you write more efficient code. This course is for all levels as long as you have a basic understanding of things like loops, functions, arrays, etc. We are writing JavaScript in this course, but about 95% of it can translate to any other language. So even if you are a Python, PHP or C# developer, you can still follow along. Basic Challenges: We start with a bunch of basic challenges that have to do with iteration and loops. Things like FizzBuzz and string reversals. These are very popular questions for entry-level interviews. We also move on to solving problems with high order array methods like filter and map. Recursion: Recursion is one of the toughest things to learn in programming. We have an entire section dedicated to it with challenges that we solve using recursion. Time & Space Complexity: We talk about how to measure an algorithm or function’s efficiency by using time and space complexity to see how the runtime and memory scale when inscreasing the input. Data Structures: Stacks, Queues, Trees, Linked Lists, Graphs, HashMaps We go over all of the common data structures and create our own implementation of them using JavaScript classes, but like I said, you could use any language. We also learn how to traverse them and complete challenges using them. Sorting Algorithms: We get into different sorting algorithms like bubble sort, insertion, selection, merge and quick sort. These are popular topics for interviews. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Assembly is cpu instructions, which perform operations on registers. In the assembly code in the post the instructions (mov) operate on registers (like rdx) and values (the numbers). On a very high level, what the code is doing is essentially moving the string "Hello World" into the register used by system calls for data, moving the value corresponding to the "print the value" operation, and then calling that system call. That's a very basic, high level overview of what the code is doing.
You need to learn about computer architecture, specifically how a cpu works and how memory is stored and managed. You also need to know how binary works and boolean algebra. For an introduction you can check out this paper from intel https://www.intel.com/content/dam/develop/external/us/en/documents/introduction-to-x64-assembly-181178.pdf. Don't worry if it doesn't make any sense, there's a lot more fundamental knowledge you are likely missing.
Assembly is the lowest level programming language you can get before it's all just 1's and 0's, and compiled programming languages get compiled into machine code (1's and 0's) by the compiler. Assembly is hard to write, and you really only need to know it if you are working on compilers or reverse engineering compiled code. It's still good to know how it works though, even if you can't actually write programs in it.
Bash is a shell, usually the default shell on linux systems. It's often the primary way of interacting with linux servers (many web servers etc. use the linux OS), and can be used interactively or through scripts. Bash scripts are great for automating things on linux because it will always be there by default, though it is not as powerful as some high level languages. Best way to learn, as with most things, is to try it out and through lots and lots of googling. Bash, and command line in general, may be a learning curve coming from primarily graphical interfaces.
If you want to learn about automation in general, I highly recommend the book Automate the Boring Stuff, for the Python language.
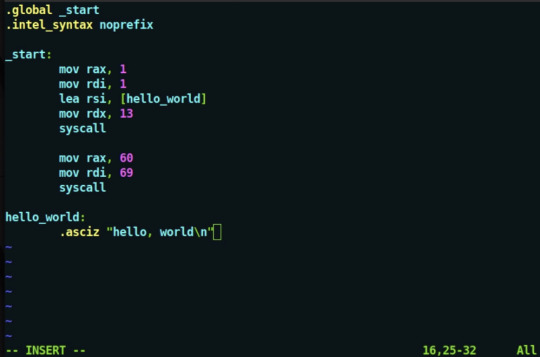
wrote my first "hello, world" in assembly today :]
i used to never ever think i was capable of programming in anything remotely close to machine code. the fact that now i have, and that i actually understand what is going on here, even in this simple code, is huge for me. i'm so proud of myself!!!
483 notes
·
View notes
Link
See the article about How to Reverse a String in Python.
#python#how to#how to reverse a string in python#string in python#programming#python tutorial#get basic idea#basic idea#basic knowledge#knowledge base
0 notes
Note
hiya foone! i'm working on the surprisingly lofty task of modding barbie fashion show 2004 and i've been told twice to ask if you have any leads on how to get to the game files. i don't know how to simplify it because i'm so in over my head at this point. here is the thread
okay so here's how you reverse engineer an arbitrary game, the quick version:
Research. Who made the game? what else did they make? Maybe they made a game with the same engine, and someone already figured out that one? (not that I saw on a quick look, but you may be able to dig deeper) Also, look in the game files. There's a PowerRender.dll and a sipEngine.bc file. Nothing for sipEngine, but PowerRender has a hit on the internet archive, maybe that download includes some info on how it encodes files?
Look at the files (with a hex editor, like HxD). KAR files seem to be the main storage mechanism, and they've got a RIFF header. RIFF is a standard, though they're not using it exactly. But this might help. Another thing you can spot in the KAR files is a bunch of english strings (CreditsTb.kar is lousy with them). That's a good sign: it means the files aren't compressed, so you don't have to figure out the compression method.
Static analysis of the EXE. Get Ghidra and load up the EXE. Find where it opens files (CreateFileA/CreateFileW on windows), trace back from there. Check the strings. Hey look, function FUN_004e6260 is called with "KAResource.kar". so FUN_004e6260 is probably a function to load arbitrary resource files. Dig through that, figure out how it works.
Dynamic analysis of the EXE. Stick it in a debugger and see what it does. Set a breakpoint on CreateFileA/W and follow the execution. I don't have a good recommendation for what tool to use here, I'm from the past. I've used Ollydbg a lot but it hasn't been updated in 9 years.
Hijack the EXE and make it do your work for you. One thing I noticed while looking around was references to Python. This game apparently embeds a python interpreter, version 2.2. Maybe you can find where it loads the code from, or inject your own code?
Anyway those are some introductory ideas. feel free to ask any follow-up questions, but this hopefully gives you some idea of where to start?
Good luck!
446 notes
·
View notes
Text
The article How to Reverse a String in Python—Different Ways Explained by Hero Vired explores various methods for reversed strings in Python. It covers techniques like slicing, loops, and the join() function. The article provides clear explanations and code examples to help readers understand and implement string reversal in Python. For More Information, Please Visit The Blog.
0 notes
Text
sorry foone but this is ridiculous. drawing out the circuitry for ADD doesn't explain a god damn thing unless you're already an electrical engineer. the explanation a beginner needs is "it adds numbers". which is the same thing + does in javascript! oh and it also adds strings there. explanation complete. (meanwhile, how do you add strings in assembly? wellll, assembly is just so simple and straightforward that that requires four loops and a call into libc to allocate new memory in the most byzantine data structure you have ever seen in your life)
and you absolutely need to understand types to use assembly. ADD can do 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit, and 64-bit addition. those are types! assembly just happens to be dynamically typed
of course it's easier to understand javascript if you know java and c++ first. and the reverse is also true. the hard part is the first language, because the hard part is learning to think about what you want as a series of very explicit discrete steps, when humans are used to handwaving away details. and if you learn C first then you are hamstrung from the beginning by having to fuck around with pointers and malloc instead of learning how to tell the computer to do something interesting
i completely reject the idea that C is a close reflection of what the computer is "really" doing, that this is important somehow, and that you are hopelessly trapped behind layers of opaque abstraction if you don't think in terms of C. it's not even portable assembly in any meaningful sense and hasn't been for a long time. if you write a loop in C then your compiler might just toss the whole thing out and use SSE instructions. and that is completely transparent to you, just like a javascript vm's use of tagged pointers is completely transparent to a javascript author.
on the contrary i posit thinking in terms of C is likely to make you slightly worse at every other language, because it keeps you from engaging with languages on their own terms. quick, does python pass arguments by value or by reference? the answer is neither, but those are the only two options in C, and i have seen so many people get hung up on that. but variables in python work fundamentally differently from variables in C!
i'm not even sure if OP was criticizing javascript or javascript tutorials here. you can definitely do some interesting galaxy-brain stuff in javascript though. it is a programming language after all
half of the mystique around "tech stuff" that most people experience is mostly just because they don't know the difference between a "tech enthusiast" as constructed by Apple et al's marketing team and "people who know computers work" and how there's very little actual overlap between these two categories. the only actually good programmers are the ones who want to fuck the computers or perchance have undergone some other technopsychosocial adaptation, which does not correlate with knowing how many dozen cameras the latest iphone has or being able to get along well with the business major interviewer at a startup called Zyergote who drives a tesla
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to traverse a string python
There are two main ways to traverse a string in Python:
Using a for loop
Using a while loop
Using a for loop
To traverse a string using a for loop, you can use the following code:
Python
my_string = "Hello, world!" for character in my_string: print(character)
This code will print each character in the string to the console.
Using a while loop
To traverse a string using a while loop, you can use the following code:
Python
my_string = "Hello, world!" index = 0 while index < len(my_string): print(my_string[index]) index += 1
This code will also print each character in the string to the console.
Which method you use to traverse a string is up to you. The for loop is generally more concise and easier to read, but the while loop can be more flexible in some cases.
Here is an example of how to use a for loop to traverse a string and reverse the order of the characters:
Python
my_string = "Hello, world!" reversed_string = "" for character in my_string[::-1]: reversed_string += character print(reversed_string)
Output:
!dlrow ,olleH
Here is an example of how to use a while loop to traverse a string and find the index of a specific character:
Python
my_string = "Hello, world!" target_character = "o" index = 0 while index < len(my_string): if my_string[index] == target_character: break index += 1 if index < len(my_string): print("The index of the character '{}' is {}.".format(target_character, index)) else: print("The character '{}' is not found in the string.".format(target_character))
Output:
The index of the character 'o' is 4.
Traversing strings is a common task in Python. By learning how to traverse strings, you will be able to write more powerful and flexible code.
#programmer#studyblr#learning to code#progblr#python#kumar's python study notes#codeblr#coding#programming
0 notes
Photo

How to Reverse a String in Python | Python Tutorial
See the article about How to Reverse a String in Python.
0 notes
Text
Nuance Decay (Software)
Nuance decay is really obvious and useful to spot in software. In normal life it is an occasional problem, but in software it is everywhere.
Why does this code do that? Why was this the best way? Why this formatting? Why this style? Why this protocol design? Why was it right to treat this edge case as an error? Why not do it this other way that seems just as good? Every bit of decision-making that went into the code, that matters but could be done differently without becoming immediately obviously wrong, broken, or worse - nuance.
The most obvious example of nuance decay in code is code copied without its comments, or seen without the commit messages or documentation which explain the rationale. So right away we can see how we can manage that kind of basic nuance decay risk: crucial information can be moved into the code, into the names or the shapes of its API, where you have to do extra work to remove it instead of extra work to keep it:
express "if you do this, that's an error" as an if statement that raises an error or as an assert;
express "doing this might do the wrong thing in ways this code can't or won't check for you" by having "unsafe" or "unportable" in the name;
and so on.
Here's a less obvious one: you write some code in a specific way to correctly handle some obscure edge-case - but you have no test to check that edge case. When someone looks at that code, if they don't think of that edge case, nuance decay has happened. This often does not matter until there's a need to change that code, but then it matters a lot. A test case stabilizes the nuance, at least within the environment of that project.
Similarly, much of "cargo culting" - copying patterns or practices without understanding how they work and why they are justified and in which contexts - can be understood as nuance decay. A good but rushed software developer sees an unfamiliar pattern in code, does their best to find or reverse-engineer a good explanation, gets to a plausible answer, and sees nothing to disprove that answer.
But I said it's everywhere, so let's go deeper - nuance decay risk almost always has one-to-one correlation with complexity, and in particular with code being badly coupled or complected together.
Any time you write some code which will do the wrong thing unless its caller or something it calls is written the right way, unless that's really obvious, that's introducing extremely "unstable" nuance, which will always decay unless we think about both the caller and called code at the same time:
A very common example is passing a reference to a mutable data object to a caller, and expecting them not to mutate it - or receiving a reference and expecting it not to be mutated concurrently. In C we fix this by having the called function make the pointed-to-object `const` in its signature (and hoping that const-correctness was not violated); in Python we can fix this by wrapping the object with a proxy that disallows mutation (and hoping that no one bypasses it with introspection or modules written in a language with no memory safety); if all else fails in most languages we can at least copy the object and hope that optimizations will eliminate the copy if it isn't needed. Notably this also reduces how complected the behavior of those two pieces of code is.
Another example is code which builds code strings - HTML, SQL, a shell command line, whatever. If you know that it will never process inputs that need escaping, you could justifiably ignore escaping. But this is also nuance - an assumption and a caveat that hovers over the code, and which is so vulnerable to decay that you have to keep actively reinforcing it in your head in order to not accidentally use the functions in an unsafe way.
Notice that these last kinds of nuances decay almost inherently can't be stabilized with comments or documentation - no amount of "this code will only work if you make sure to pass in only the right inputs!" warnings will free you from the work of remembering those warnings.
You must hold this extra complexity, these extra caveats, these extra wrinkles of nuance about how to use this code, in your head, every time you use it - or else your code might be broken or even dangerously hackable and you won't even know.
So:
Nuance decay gives you a pretty good way to answer "should I change the code shape? or change the names? or at least add a comment here?" - or in other words, "is this self-descriptive enough?" Just ask yourself - if someone doesn't know why I'm (not) doing this, and they had to figure it out from context, would they get the wrong idea?
Nuance decay is a very powerful idea for predicting readability and maintainability problems in your code, especially the ones caused by implicit assumptions and unnecessary complexity, because it centers "what information must come along with this code to use it correctly and keep it correct?"
14 notes
·
View notes
Photo





Do you know how to reverse a string in python? If no, then no problem we have different ways to do so.
Reverse of a string is means simply writing the string from last to the first index in a reverse manner. Likewise, the reverse of “python” will be “nohtyp”.
There are 4 different methods to reverse a string
#python#python3#pythonforbeginners#python language#pythonlearning#pythonprogramming#pythonprogramminglanguage#pythoncode#pythoncoding#codingforteens#codingforbeginners#coding for kids#pythondeveloper#webdevelopment#datascience#computerscience#technology#python tutorial#python course#pythontraining#reverseprogram#recursion#recursioninpython#learntocode#learntoprogram#learncoding#html#java#pythondjango#pythonstring
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
CSS MINIFIER THE BEST TOOLS

CSS MINIFIER The Best Tools
css minifier api command line npm webpack php node to normal offline minify and compress compressor js wordpress plugin online javascript bootstrap babel best beautifier browser brackets comparison check closure code download de decompressor decompress dreamweaver
directory drupal expand minified error explained express email example eclipse file for from format github gulp generator grunt html htaccess helps with multiple option how inverse @import in visual studio phpstorm java codeigniter keep comments library by laravel mix linux liquid media query map
mac means magento 2 modules maven method notepad++ normalize tool on options python postcss performance reverse remove rollup reset regex rails readable stack overflow sass shopify sublime text 3 style size single unminify uglify un using upload ubuntu url vscode 2017 & version 4 windows without
yii2 files package minify-css-string 5 script php-html-css-js-minifier.php topic nodejs convert change converter vs minify_css_compressor netbeans 8.2 apache way c# extension free exclude gradle gulpfile.js css/javascript next string your asp.net cara gtmetrix minifying joomla resources (html javascript)
wp rocket yslow css/bootstrap.min.css bootstrap.min.css not cdn beautify prettify minification unknown kaios django function software spaces tools gzip break whitespace checker yui-compressor ve nedir minimize cc 8 7 cannot read property 'length' of undefined find module 'is-obj' expected a
pseudo-class or pseudo-element postcss-svgo missed semicolon 'type' 'trim' lexical 1 unrecognized the can reduce network payload sizes compare dev/css/minify combine divi w3 total cache task minifies gulp-sass concat all rename gulp-clean-css clean gulp-minify-css working names special scss watch
css-html-js-minify nginx which attribute brainly benefits bash button css.com class cli document difference google loader one meaning minify_css middleman build server react terminal tutorial 2019 2015 create (minify) zend framework opencart symfony
#html#css#cssminifier#coding#htmlparse#ruby#vscode#flex css#css display grid#css grid layout#column grid#tag css#grid css#html & css
3 notes
·
View notes